By the long-afforded Viscose fabric, the textile industry is regarded as high-class, luxurious, versatile, and affordable. But how does this wonderful fabric come into being? In this article, we will embark on a journey into the production of viscose, shedding light on one of the most widely used fabrics in the world. Originating from natural cellulose till it is finally converted into this soft, breathable fabric, we shall view the creation of viscose in terms of science, artistry, and innovation. Suppose you are a fashion buff, a sustainability advocate, or simply curious about which textiles are shaping daily life. In that case, this article will provide you with a clear insight into the exceptional standing the viscose fabric holds in the modern textile world—and why it remains a key source of designer wear manufacturing.
The History of Viscose and Its Evolution
Rayon was first developed in the late 19th century as a cheaper substitute for silk. The origins date back to 1855, when chemist Georges Audemars began experimenting with artificial silk made from cellulose. A much more practical and commercializable process for making viscose, though, had to wait until 1891, when it was patented by British scientists Charles Cross, Edward Bevan, and Clayton Beadle.
Commercial production of viscose began around the turn of the 20th century, revolutionizing the textile industry with an affordable and versatile material. Over the years, improvements to the viscose manufacturing process have enhanced its quality, making it an excellent product for use in apparel, upholstery, and household articles. Nowadays, viscose development is closely tied to efforts to find greener ways to reduce its environmental footprint.
Rise in Popularity and Key Milestones
It is the low price, the pliability of use, and the silkiness of the feel that make viscose the preferred fiber in common textile usage. One important historical milestone was the introduction of rayon garments to the market in the 1920s, causing significant upheaval in the world of fashion as they provided an affordable alternative to the costly natural fibers, such as silk. Over the decades, improvements in manufacturing technologies have increased production efficiencies and expanded the applications of viscose, from garments to industrial-grade products.
More recently, the theme of sustainability has taken center stage, with eco-conscious prize holders demanding greener viscose production. Through innovations such as the closed-loop production system and the use of sustainable raw materials, viscose has been given a promising future in the transition to greener textiles. Today, big brands and manufacturers continue to invest in research and apply these new technologies, thereby keeping the viscose paradigm at the forefront of the global textile industry.
Evolution of Production Techniques Over the Decades
At some point in the past, the technique of manufacturing textiles, particularly viscose, underwent a significant transformation. The early ones were perhaps the old processes, which were chemically intensive and had environmental and health hazards. Low technology and little concern for the world’s sustainability gave way to more environmentally friendly practices.
Key Improvements:
- Closed-loop systems that capture and reuse solvents in manufacturing to reduce chemical waste
- Alternative raw materials, such as wood pulp from certified sustainable forests
- Minimizing the impact of deforestation
The innovations mentioned above not only address ecological concerns but also align with the growing consumer sentiment for accountability and transparency in the textile supply chain.
Understanding the Viscose Manufacturing Process
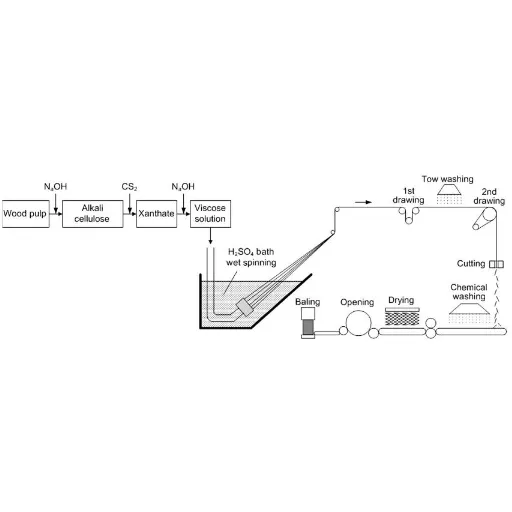
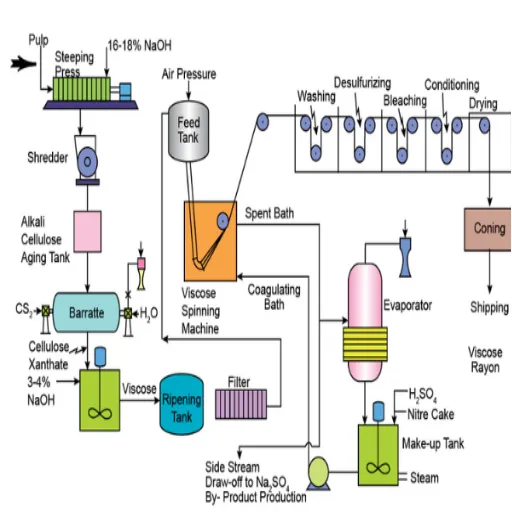
The entire viscose manufacturing process begins with raw materials, primarily wood pulp, which are sourced from sustainable forests whenever possible. The pulp is dipped or treated in certain chemicals, such as sodium hydroxide or carbon disulfide, to form a solution of viscose. This solution is then pushed through spinnerets—small holes—into an acid bath, where the solution eventually solidifies into fibers. Once formed, fibers go through washing, purification, and sometimes further processing to achieve the desired characteristics. The entire process converts natural materials into the versatile textile known as viscose, best recognized for its soft and breathable properties.
Raw Materials: Sourcing Cellulose and Key Stages
Sourcing of cellulose is the primary step in viscose manufacturing, with wood pulp or cotton linters being the usual raw materials. These raw materials are selected for being rich sources of cellulose, the basic ingredient required for viscose fiber production. Sustainability is receiving more attention today, with many mills seeking wood from certified forests or cotton linters as waste by-products.
Manufacturing Steps:
- Treatment with sodium hydroxide: Cellulose is treated to obtain alkalized cellulose
- Chemical reaction: Reacted with carbon disulfide to produce a golden-yellow viscose solution
- Filtering and aging: The solution is filtered and allowed to age until it reaches a suitable viscosity
- Spinning: Solution is spun into fibers through a spinneret
- Solidification: Fibers solidify after extrusion into an acid bath
- Final processing: Fibers are washed, purified, and strengthened through various treatments
Challenges in Viscose Production
Viscose has environmental and industrial drawbacks. First, carbon disulfide is used in the production process, which is toxic in nature and can potentially harm the health of the workers; air emission levels are another concern. Additionally, large amounts of water containing residues of harmful chemicals are generated by the production process and can be a significant source of water pollution if discharged without proper treatment.
Secondly, energy is another major factor. The production process requires a substantial amount of energy, which significantly contributes to the carbon footprint.
Industry Response:
With the growing global awareness of sustainability, the demand for stricter regulations and greener alternatives has also increased. Companies are making efforts to develop closed-loop production systems and novel technologies to address these issues and reduce the environmental harm associated with viscose production. However, such upgrades require a capital-intensive process, thus making the entire industry slow to adopt the changes, especially at smaller scales.
Market Demand and Applications of Viscose Fabric

It has been increasingly demanded because it is versatile, very affordable, and can imitate natural fibers such as cotton or silk. In the fashion industry, viscose is widely used to manufacture lightweight, breathable, soft garments such as dresses, blouses, and casual wear. Additionally, it has been well accepted by the home textile sector, with products such as curtains, upholstery, and bed linens, where viscosity helps enhance the smoothness of the fabric or facilitates blending with other materials. The rising demand for sustainable and biodegradable materials has generated increased interest in responsibly sourced viscose, making it relevant to both conventional and eco-friendly markets.
Viscose in Fashion: Versatile Applications
As the fiber conveys style, comfort, and versatility, viscose has been considered a global fashion staple for ages. Search trends over time reveal increasing interest in viscose as people prefer lightweight and breathable fabric for warmer climates. The popular keywords highlight seasonal collections, including summer dresses, flowing skirts, and breathable tops.
Another key point in discussions is sustainable viscose made from fibers obtained from responsibly managed forests, thereby serving the conscience of an increasingly eco-aware consumer who wants both beauty and ethical sourcing. Increased search activity regarding these points highlights their practicality and contributes to a greater awareness of sustainable fashion.
Industrial Uses of Viscose Fiber
| Application Area | Products | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Home Furnishings | Curtains, upholstery, bed linens | Soft feel, beautiful appearance |
| Industrial Applications | Tire cords, nonwovens | Tensile strength, biodegradability |
| Packaging Industry | Sustainable packaging materials | Environmental benefits, biodegradability |
Ranking viscose fiber highest in the industry due to its versatility and adaptability, it is suitable for a wide range of other applications. Recent search engine data indicate the widespread use of fabric-making for home furnishings, such as curtains, upholstery, and bed linens, where preference is given to its soft feel and beautiful appearance. Besides textiles, the sector for tire cords and nonwovens is rapidly growing into another application for viscose due to its tensile strength and biodegradability. Search trends indicate that viscose is gaining popularity in the packaging industry, which is encouraging the sustainable path that industries are taking. This upsurge acknowledges not only its operational benefits but also the paradigm shift in societal preference for sustainable and innovative options.
Innovations in Sustainable Viscose Manufacturing

They are trying to improve viscose production so that the environment is better protected and product quality is not compromised. Closed-loop system developments include recycling chemicals and water, resulting in minimal waste and pollution generation. Certified raw materials often come from sustainably managed forests, thus limiting the rate at which forests are destroyed. Researchers are also attempting to use alternative feedstocks, such as agricultural residues, to reduce their reliance on conventional feedstocks. Together, all these efforts promote a greener production process.
Closed-Loop Production Systems
Closed-loop production mechanisms facilitate waste elimination by continuously utilizing resources, thereby supporting the concept of a circular economy. The recycling of materials, coupled with reuse approaches, renders the systems highly efficient in terms of resource utilization and environmentally friendly.
Recent advances include AI-powered material tracking, automatic sorting, and decision-making for potential reuse applications, offering manufacturers new and improved methods for recovering and repurposing materials. Recent statistics display significant bi-fold decreases in resource consumption and waste generation in industries that adopt closed-loop methods, portraying it as a significant viable way toward sustainable growth.
The systems showcase immense potential to bring about a paradigm shift in how products are made, thus acting as a catalyst for worldwide efforts to reduce ecological footprints.
Sustainable Raw Materials and Innovations
Now, as many sectors become aware of their carbon footprints, it has become imperative to examine the supply side using sustainable raw materials. These materials typically include bamboo and recycled metals and bioplastics, which are either harvested or processed in a way that minimizes environmental damage.
Recent Developments:
- Biodegradable composites and renewable alternatives
- Algae-based polymers for the packaging and textile industries
- Greener production cycles and circular economy concepts
- Displacement of scarce natural resources
Biodegradable composites and renewable alternatives have been further developed in the realm of material sciences to meet performance standards while addressing sustainability issues. To cite a vivid example, recently developed algae-based polymers have opened promising avenues for the packaging and textile industries, thereby enabling greener production cycles. Industries equipped with such raw materials and technologies are therefore able to promote circular economy concepts and the displacement of scarce natural resources.
Future Trends in Viscose Manufacturing

Future trends in viscose manufacturing highlight sustainability and minimizing environmental impact. Key developments are closed loops, where, during production, chemicals are recovered and reused, thereby severely reducing pollution. Furthermore, alternative raw materials such as recycled textiles or wood from sustainable sources are being utilized to ensure that the entire production process adheres to environmentally friendly standards. On the other hand, new technologies, such as enzyme-based treatments, are being developed to treat viscose in a more efficient and environmentally friendly manner. These emerging trends represent a united effort to ensure the environmentally conscious production of high-grade viscose.
Integration of Technology in Production
The integration of advanced technology in production processes has transformed different industries. For instance, machinery and AI-based systems optimize the production line to ensure precision and wastage minimization. Innovative technology monitors real-time activities using an analytical approach through IoT sensors, enabling manufacturers to identify inefficient activities and provide improvements in high-quality standards.
Moreover, machine learning algorithms predict maintenance needs for machinery to prevent downtime. These advancements increase productivity and are environmentally friendly, thus positioning the modern producer as forward-thinking.
Consumer Demand for Sustainable and Ethical Practices
Being a consumer, I recognize the importance of sustainably and ethically produced goods. Whenever I am aware that a company has implemented environmentally friendly processes and ensures fair labor conditions, I go ahead and buy its goods. These values reflect social responsibility, as well as a vision for the future of humans and the earth.
Reference Sources
Here are five professional and authoritative sources related to “viscose manufacturing” to check if the contents of your article are indeed correct:
- Sustainability in the Production of Rayon
This document addresses the sustainability issues in rayon (viscose) production, including the use of chemicals and their environmental impacts. - Fake Silk: The Lethal History of Viscose Rayon
A history of the creation of viscose rayon, its uses, and associated health and environmental concerns. - Viscose – An Overview (ScienceDirect)
Extensive explanations of the viscose production process, covering the chemical conversion of cellulose into spinnable fibers. - A Review on Raw Materials, Commercial Production, and Environmental Impact
The review encompasses the raw materials, production methods, and environmental considerations of viscose manufacturing. - Textile Materials Explained – Green Jax Project
Source for explaining the environmental and health hazards of viscose production, including comparisons with other textile materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is viscose manufacturing?
Viscose manufacturing is the process of producing viscose rayon, a type of semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose. The manufacturing process involves dissolving cellulose from wood pulp or other plant materials in a chemical solution to create a viscous liquid, which is then extruded through a spinneret to form filaments. These filaments are spun into yarn and woven into fabrics.
How is viscose rayon produced?
The production of viscose rayon involves several steps, beginning with the shredding of cellulose into small pieces. This cellulose is then dissolved in caustic soda to form alkali cellulose, which is treated with carbon disulfide to create cellulose xanthate. The resulting solution is aged and then extruded through a spinneret into a spin bath, where it is regenerated into filament yarn.
What are the primary raw materials used in viscose manufacturing?
The primary raw material for viscose manufacturing is cellulose, which is derived from wood pulp, cotton linters, or other cellulosic fibers. Chemicals such as caustic soda, carbon disulfide, and sulfuric acid are also used in the process to facilitate the dissolution and regeneration of cellulose.
What are the environmental impacts of viscose manufacturing?
The environmental impact of viscose manufacturing can be significant due to the use of hazardous chemicals such as carbon disulfide and caustic soda. However, advancements in sustainable practices, such as closed-loop systems and the development of lyocell—a more environmentally friendly alternative—are helping to reduce these impacts.
What type of fabric is made from viscose?
Viscose is used to create a variety of fabrics, often characterized by their softness and drape. Standard fabrics made from viscose include rayon, a lightweight and breathable material suitable for clothing, curtains, and upholstery.
How does the viscose process differ from other fiber manufacturing methods?
The viscose process differs from other fiber manufacturing methods, such as polyester or cuprammonium rayon production, primarily in its use of natural cellulose as a raw material. Unlike synthetic fibers, viscose is derived from renewable sources, offering a more sustainable alternative when produced responsibly.
What are rayon filaments, and how are they used?
Rayon filaments are long, continuous strands of regenerated cellulose created during the viscose manufacturing process. These filaments can be woven into various textiles and are often used in clothing manufacturing due to their silk-like appearance and feel, making them a popular choice for garments.
Can viscose be used as a substitute for silk?
Yes, viscose can be used as an alternative to silk due to its similar texture and drape. It is often chosen for its affordability and versatility, making it a popular choice in the fashion industry for producing lightweight garments and luxurious-looking fabrics.
What are some typical applications for viscose garments?
Viscose garments are widely used in the fashion industry due to their absorbent properties and comfortable feel against the skin. They are commonly found in dresses, blouses, linings, and other clothing items where a soft, flowing fabric is desired.



















