Viscose rayon has become the silk alternative, a term for modern fibers that can be spun into a wide range of products, from soft clothes to carpet linings. But how does one create this smooth, breathable fiber? The viscose manufacturing process is based on a brilliant combination of science and innovation, wherein natural cellulose is transformed into an elegant fabric that balances style, comfort, and utility. This blog post delves into the details of how viscose fiber is produced by examining all the steps involved in its manufacture and addressing the environmental concerns associated with the process. Whether you’re a fashion enthusiast, a sustainability advocate, or someone who simply loves to learn about the manufacturing process, this guide promises to be an informative and engaging read. Get ready to uncover the story behind viscose rayon, a remarkable blend that bridges the gap between nature and technology.
🧬 Introduction to Viscose Fiber
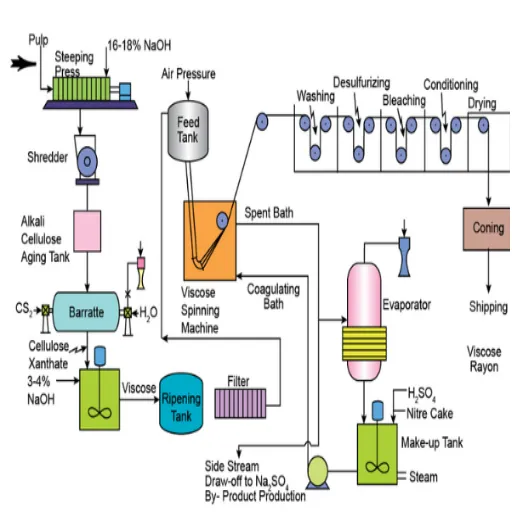
Viscose fiber is a semi-synthetic material derived from cellulose, usually obtained from wood pulp. The manufacturing process includes dissolving the cellulose in chemicals to create a soluble compound, which is then regenerated into fibers. Being more natural yet possessing a silk-like feel and high flexibility, viscose is primarily used in textiles for clothing and upholstery. While the process itself suggests a slightly more natural alternative to synthetic ones, some negative aspects can be considered, such as environmental hazards associated with the chemicals used and increased water consumption.
📚 Definition and Significance of Viscose Fiber
Viscose fiber, usually called rayon, is a semi-synthetic material made from cellulose, generally derived from wood pulp or cotton. With a smooth and light feel, it has an excellent sense of natural fibers, such as silk or cotton, and is an eco-friendly choice among fashion and home textiles. Its yield versatility makes it suitable for a broad range of applications, from breathable summer wear to heavy upholstery fabrics.
⚠️ Environmental Considerations
A drawback, however, has been the environmental harm associated with its manufacture, with heavy chemical usage and consequent water pollution. In other words, new developments have emerged regarding greener production methods for viscose, including a closed-loop process that nearly eliminates waste and ensures solvent recycling. The idea behind these developments is to mitigate environmental harm while retaining the best attributes of viscose, striking a balance between performance and environmental impact.
⚙️ Overview of the Viscose Manufacturing Process
Manufacturing Steps
- Cellulose Preparation: Cellulose, typically obtained from wood pulp, is reacted with chemicals, such as sodium hydroxide, to form alkali cellulose.
- Aging Process: The alkali cellulose is aged under controlled conditions to increase its reactivity.
- Xanthation: After aging, the alkali cellulose is reacted with carbon disulfide to form cellulose xanthate.
- Dissolution: The compound so obtained is then dissolved in a diluted solution of sodium hydroxide to create a heavy, syrupy fluid called viscose.
- Processing: The viscose is filtered, degassed, and extruded through spinnerets into an acid bath of sulfuric acid, where it is regenerated and then solidified into an amorphous solid.
🌱 Modern Sustainability Improvements
In recent times, the industry has focused on making the process more environmentally friendly. Very modern closed-loop systems now exist, which enable the recovery and recycling of chemicals used in the process, resulting in a significant reduction in waste and emissions. With these steps in place, viscose production can therefore be firmly aligned with sustainability without compromising its versatility in application.
🧪 Chemical Properties of Viscose Fiber

Here are some other chemical characteristics that make the fiber versatile:
♻️ Biodegradability
Viscose, based on natural cellulose, is biodegradable and environmentally friendly under suitable conditions.
💧 Moisture Absorption
The fiber has a high moisture absorption characteristic. This allows it to absorb water and retain moisture, which enhances comfort in apparel applications.
⚗️ Chemical Reactivity
It reacts with powerful acids and bases. Alkali treatment would weaken the fibers. Thus, in chemical environments, the fiber must be handled with caution.
🌡️ Thermal Sensitivity
The fiber is sensitive to heat, with a potential for shrinkage in its structural arrangement.
🎨 Affinity for Dyes
It exhibits a strong affinity for dyes, enabling the fiber to absorb dye quickly and produce a bright color.
Understanding the Chemical Composition
The primary component of viscose is regenerated cellulose, a biopolymer derived from natural sources such as wood pulp or cotton linters. In the chemical treatment, cellulose is treated in the presence of an alkali and carbon disulfide to yield viscose, a soluble compound that can be spun into fibers. It is for this very reason that viscose is classified as semi-synthetic, being a bridge between natural and synthetic fibers. Modern technology has since introduced methods for producing the fiber in a more environmentally friendly manner, thereby addressing issues related to its chemicals and ecological hazards. Understanding the composition of viscose materials will allow their applications in textiles to be enhanced, from clothing that breathes to flexible home furnishings.
Impact of Chemicals Used in Production
Several toxic chemical materials, the chief among them being sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide, are involved in guaranteeing the production of viscose. Sodium hydroxide, useful in breaking down cellulose, may cause water pollution when discharged during production. Carbon disulfide is hazardous to workers in manufacturing settings due to its toxicity and represents a significant environmental concern when released into the air. The development of greener processes under closed-loop systems promises to slash chemical leakage and recycle chemicals effectively. The approach to offsetting the ecological footprint of viscose production is therefore transforming greater sustainability, thereby raising concerns about public and environmental health.
🔬 Physical Properties of Viscose Fibers
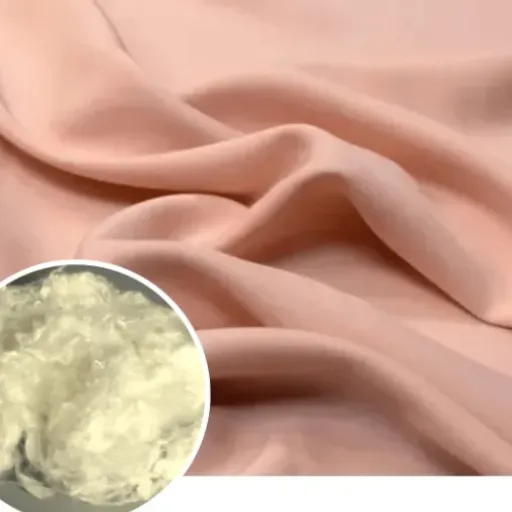

One of the defining attributes of viscose fibers is their smooth touch, also known as a soft, natural feel, or good breathability, which is somewhat akin to that of cotton or silk. With excellent moisture absorption ability, it keeps the wearer cool and comfortable. Viscose fibers possess this sheen themselves, a desirable trait indeed. Some synthetics might be slightly stronger than them, but the yarns are very prone to wilting and losing all strength in water, hence the need for gentle handling during washing. These characteristics do make viscose suitable for comfortable, weightless clothing and fabrics.
Texture and Breathability
Due to its unique texture, viscose has a wide range of versatile uses in fashion and design. It is soft and smooth, often cuddled with silk for a glorious finish. Thus, it can be used in designing clothes that need to be comfortable and elegant. It is breathable, making it ideal for use in creating active wear or attire for a hot climate. Viscose, being a good conductor of moisture, renders the cooling effect, ensuring the wearer’s comfort. For these reasons, the color of viscose has continued to be a matter of textile research in recent times, highlighting the considerable attraction of the fabric to both style and functionality.
Durability and Care Instructions
Viscose is a moderately durable fabric but demands attentive care to maintain its quality and longevity. Recent data trends from search engines suggest that many users are seeking the proper methods for caring for viscose garments.
Care Guidelines:
- Wash by hand in cold water with a gentle detergent or use a delicate cycle on the washing machine.
- Never wring or twist the garment, as doing so would only serve to break down the fibres.
- Do not put it in the dryer; instead, lay it flat to dry so that it retains its shape.
- Iron on low settings with a cloth placed between the iron and the fabric to prevent direct heat
Viscose garments will retain their flowing elegance and pleasant feel when cared for in this manner, which has significantly contributed to their continued popularity to this day.
🎯 End Uses of Viscose Fiber

Being versatile and comfortable, viscose fiber has more end uses than any other fiber in the construction industry. The following comprise common end uses.
| Category | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| 👗 Apparel | Dresses, blouses, linings, and lightweight suits | Soft to the touch, and allows the skin to breathe |
| 🏠 Home Textiles | Curtains, upholstery, bed linens, and decorative pillows | Elegant drape and silky finish |
| 🧻 Non-Woven Products | Sanitary products, medical wipes, and cleaning cloths | High absorbency properties |
| 🏭 Industrial Applications | Tire cord and packaging materials | Added strength and flexibility |
Applications in Fashion
Due to its versatility and beautiful drapes, viscose has almost always played a crucial role in the fashion field. Based on recent search trends, customers frequently ask about its use in contemporary garments. Viscose is most sought after for producing lightweight clothes, such as dresses, blouses, and skirts, that offer great comfort and elegance. Designers utilize a viscose blend to create soft, breathable, and drapey clothing that appeals to a wide range of customers. It is also noteworthy for its use in activewear or lingerie, thanks to its moisture-wicking capability and smooth surface, which is gentle on the skin. This versatility-with-style trait places it at the forefront of every fashionable choice in the everyday or high-fashion world.
Home Textiles and Industrial Uses
Viscose has been utilized in various areas of textile application for the home, ranging from curtains to upholstery and bedding. Its softness and resemblance to natural fibers put viscose in a position of choice to produce luxuriously affordable household items. In interior applications, the dye-absorbing capability of viscose ensures bright and long-lasting colors.
On the industrial front, viscose is often labeled for its adaptability and strength. It is suitable for manufacturers of sanitary products, tire cords, and other similar materials — really, it absorbs moisture and biodegrades. Such features are utilized across a broad spectrum of industrial and commercial sectors. This ability to be used in both home and industrial sectors establishes viscose as a highly sought-after material due to its practicality and sustainability.
⚠️ Challenges in the Viscose Manufacturing Process

The viscose process presents several challenges that are pertinent to efficiency and sustainability. The production is an opportunity to present toxic chemicals, such as carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide. Therefore, it may pose health risks to workers and the environment unless properly controlled. Water and power are consumed in large quantities during the process, thus presenting concerns for the environment. Another problem is the disposal of waste, as byproducts must be disposed of properly to prevent them from becoming sources of emissions and pollution. This implies the need for implementing better practices and innovations to achieve an eco-friendly and safe process.
🌍 Environmental Concerns
Environmental concerns are escalating in tandem with industrial issues, including emissions and resource consumption. Recent data have shown search trends reflecting the ever-increasing user interest in sustainable practices and eco-innovations.
Some of the most frequent questions on the Internet are “How can industries reduce their carbon footprints?” or “What are the alternatives to harmful chemical processes?”
Meanwhile, these trends support the push for the development of renewable energy, a reduction in reliance on hazardous materials, and environmental regulations. Bearing in mind all these issues, industries are therefore compelled to upgrade their technology, increase efficiency, and minimize environmental impact as they operate, to meet the needs of both people and regulatory requirements.
💰 Economic Considerations
Hence, I consider economic factors to be an essential consideration that affects all types of industrial decision-making. Balancing profitability and spending towards sustainable technologies is what really dictates the long-term survival of an industrial concern. Emphasizing higher efficiency and innovation entails going beyond cost reduction and acts as support for economic growth and new opportunities to remain competitive. Click here to read more.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the viscose fibre manufacturing process?
The viscose fibre manufacturing process involves several key steps, including the preparation of cellulose, xanthation, and the creation of a viscose solution. The cellulose is treated with caustic soda, then aged to form alkali cellulose crumbs. These crumbs are dissolved in carbon disulfide to produce the viscose solution, which is then ripened before being extruded through a spinneret to form rayon filaments.
How is the viscose solution prepared?
The preparation of the viscose solution begins with steeping cellulose in a sodium hydroxide solution to create alkali cellulose. This material is then subjected to xanthation using carbon disulfide, which transforms it into a viscose solution. The ripened viscose solution is then ready for the spinning process, where it can be extruded to form fibers.
What are the steps involved in producing rayon?
The rayon production process includes several stages: the preparation of cellulose, xanthation, dissolution in carbon disulfide, ripening of the viscose solution, and spinning through a spinneret. The solution is then forced into a spinning bath where the fibers solidify, followed by washing and drying to achieve the desired moisture content.
What is the role of the spinneret in the viscose fibre manufacturing process?
The spinneret plays a crucial role in the viscose fibre manufacturing process as it is the device through which the ripened viscose solution is extruded. The solution is forced through fine holes in the spinneret, allowing it to form continuous filaments that will be solidified in the spinning bath.
What are the properties of viscose rayon?
Viscose rayon, often referred to as artificial silk, possesses several desirable properties. It is known for its smooth texture, high absorbency, and ease of dyeing. Additionally, viscose fibers exhibit good breathability, making them suitable for various rayon fabrics used in the textile industry.
How does the degree of polymerization affect viscose fiber?
The degree of polymerization has a direct influence on the properties of viscose fibers. A higher degree of polymerization results in stronger and more durable fibers, while a lower degree can lead to weaker, less resilient fibers. This factor is critical in determining the end-use applications of rayon fabrics.
What are the environmental impacts of viscose fiber manufacturing?
The viscose fiber manufacturing process can have significant environmental impacts, particularly due to the use of chemicals such as carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide. Proper management and treatment of waste products are crucial to minimizing pollution and ensuring sustainable practices within the viscose industry.
What are the common uses of rayon fabrics?
Rayon fabrics are versatile and widely used in the textile industry for a variety of applications. Typical uses include clothing, home textiles, and upholstery. Due to their soft texture and excellent dyeability, rayon fabrics are often favored for garments that require a luxurious feel and aesthetic appeal.
How do viscose fibers compare to other textile fibers?
Viscose fibers are often compared to other textile fibers such as cotton and polyester. They are softer and more absorbent than polyester, making them more comfortable to wear. However, they may not be as durable as synthetic fibers. Their ability to mimic the properties of natural fibers while being produced through a man-made process makes them a unique option in the textile market.
📚 Reference Sources
Here are five authentic and professional references that one could use to verify the information in your article on “viscose fibre manufacturing process”:
- The Historical Development of and the Outlook for Viscose Fibres
Gives a detailed historical aspect of the evolution and manufacture of viscose fibres and the significance of viscose from an industry point of view. - World Production of Viscose Fibres
Treats global production trends of viscose fibres with attention to the chemical fibre industry and its regional dynamics. - The Manufacture of Viscose Rayon Fibres
Details the chemical processes for producing viscose rayon fibres and fibre-making techniques. - Fake Silk: The Lethal History of Viscose Rayon
Details the manufacturing steps of viscose rayon from an industrial perspective, with a historical overview and an examination of its health and environmental impacts. - Carbon Disulphide and Hydrogen Sulphide Emissions from Viscose Fibre Manufacturing Industry: A Case Study in India
This case study examines the environmental impact of viscose fibre manufacturing, focusing on emissions and sustainability challenges.



















